Hygiene Monitoring at Critical Control Points (HACCP)
Industry
For managers and operators of water systems as part of industrial operation or water utility, performing hazard analysis and critical control point monitoring, or HACCP, is paramount to ensuring in a timely manner that end products do not pose a hazard to workers, residents and other stakeholders.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic preventive approach to food and water safety that provides a methodology to identify, evaluate, and minimize or control microbial hazards. With the goal of preventing, eliminating and/or reducing hazards to an acceptable level, it’s critical that the supervisory members of any HACCP team are at least familiar with the methodology, which includes five preliminary steps and seven principles.
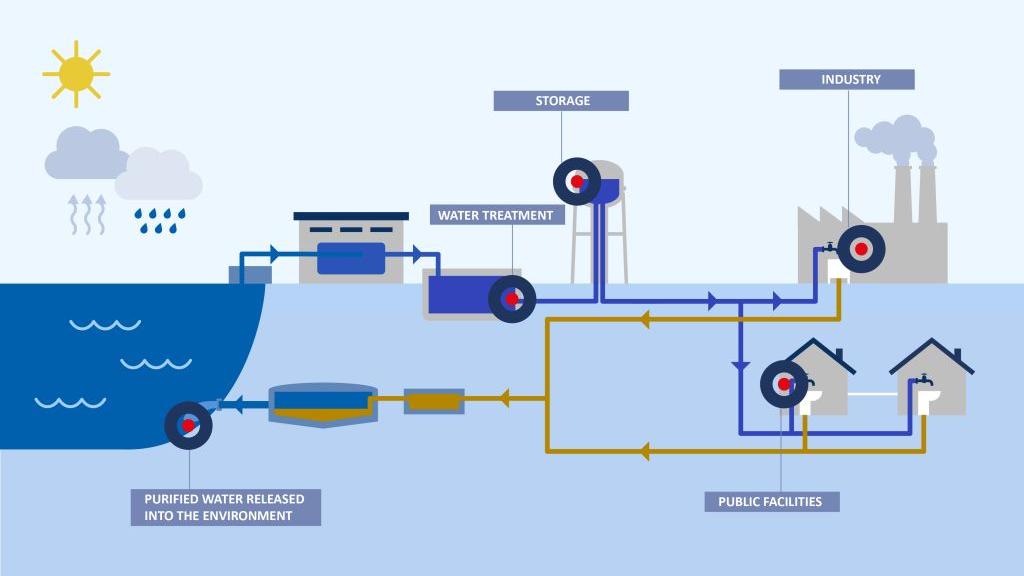
These principles are equally relevant for water utilities and wastewater treatment plants. Rain events, floods, leaks in pipes and reservoirs, equipment failures and treatment process failures can lead to the contamination of drinking water with pathogenic bacteria. Because E. coli bacteria are present in feces of all warm-blooded animals, they are generally used as an indicator for fecal contamination. [1]
At rqmicro, we have developed tests that enable operators in the food and beverage industry, bottling plants, and water treatment plants to monitor the presence of bioburden in water and relevant pathogens such as Legionella and E. coli. Accurate and reliable results are generated on-site or in labs within 30 minutes to two hours. Our tests can be implemented seamlessly as part of your established HACCP protocols.
The advantage of following a HACCP protocol based on rqmicro technology include:
-
Rapid detection of microbial contamination in the water industry and in food and beverage production
-
Quantitative assessment and corresponding response parameters - total viable bacteria and specific pathogens such as E. coli or Legionella
-
Reliable internal quality control based on intact cell counts and fast release of end products
-
Cost-effective self-inspection tool to complement official tests
-
Implementation of effective procedures to mitigate health, operational, financial and regulatory risks
Unfortunately, E. coli outbreaks still happen from time to time. For example, at the 2021 Tokyo Olympics, the outdoor venue for triathlon was heavily polluted by E. coli and athletes were sick afterwards. The reason why an E. coli outbreak is not easy to prevent is that E. coli pollution can come from many sources. Animal waste from a farm, leakage in a city’s drainage system, improper treatment of sewage, poorly managed wastewater discharge could be possible sources.
Frequent and fast testing is the key to prevent reputational and financial damage. Learn more about the rqmicro.COUNT tests that we provide for water system operators or contact us today.
Benefits
Recommended for You:

Hygiene Monitoring in Food Safety and Water Systems
At rqmicro, we have developed tests that can be implemented seamlessly as part of your established HACCP protocols.

Wastewater Reuse
rqmicro.COUNT enables effective quality control and risk assessment in wastewater reuse applications.
[1] Odonkor, S. T., & Ampofo, J. K. (2013). Escherichia coli as an indicator of bacteriological quality of water: an overview. Microbiology Research, 4(1), e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/mr.2013.e2