This blog post summarizes the panel discussion with guest speaker Philipp Witzel, Sales Engineer at innowac, and Silvana Gloor, Application Specialist at rqmicro. Philipp unfolds the story of their experiences with rqmicro.COUNT for industrial cooling tower monitoring and discusses the impact of rqmicro.COUNT on their customers’ day-to-day business. The rqmicro solution serves as an early warning system, aiding in preventive measures and enhancing the effectiveness of biocides.
Picture 1: Click on the picture to watch the recorded version of the webinar.
About innowac
Founded in 1998, innowac initially focused on cooling and boiler water treatment. Over the years, its expertise expanded, culminating in a diverse portfolio of water treatment solutions. A pivotal moment came in 2021 when innowac joined the EnviroWater Group, broadening its network of water experts. Today, innowac offers a comprehensive set of solutions covering cooling water and boiler water treatment, process additives, process water, wastewater, and dust control.
VDI Guidelines Include Rapid Testing of Legionella with rqmicro.COUNT
Before Philipp Witzel talked about his experiences with rqmicro.COUNT, he provided a brief overview of the 42nd BImSchV and VDI 2047. Compliance with these standards ensures the safe operation of evaporative cooling systems and sets Legionella concentration limits, prompting timely interventions to maintain water quality. The guidelines specifically include the analytical method which is automated within the rqmicro.COUNT instrument.
The rqmicro.COUNT device has streamlined processes, offering almost real-time insights into cooling water conditions. The speed of results and its applicability in industry make it an invaluable tool for both innowac and its customers.
Integrating rqmicro.COUNT as an Early Warning System
Philipp describes the project goals and the decision-making process behind choosing rqmicro.COUNT and adds, that the need for rapid and reliable results is recognized not only in companies, but also in the water treatment industry. The goal was to find a solution that could perform in cooling water, which has a different matrix compared to drinking water. As Philipp said, their experience has shown that sample preparation is important to keep measurement uncertainties low. After exploring options, innowac discovered rqmicro.COUNT and conducted initial tests, which led to the decision to deploy the device.
In the end, rqmicro.COUNT was integrated into their daily workflow. Periodic analyses are conducted for specific customers, involving on-site sample collection, and immediate lab analysis to minimize the time between sampling and assessment. The device plays a key role in monitoring existing dosages and systems, acting as an early warning system to promptly address any issues. This integration is seen as a proactive strategy to ensure the efficiency of water treatment practices for their selected customers.

Picture 2: rqmicro.COUNT instrument installed in the innowac facility.
Understanding Viable But Non-Culturable Bacteria (VBNC) in Cooling Water
In their conversation, Silvana and Philipp discuss the differences in measurement units between rqmicro.COUNT, based on flow cytometry and the traditional plating method. Essentially, flow cytometry counts every single viable cell, including those in the viable but non-culturable (VBNC) state. Philipp draws attention to the detection of VBNC bacteria by rqmicro.COUNT that would not be found on the traditional plate. In systems with routine measurements, the gap between plating and rqmicro.COUNT results is small. However, Philipp highlights cases where the gap was larger, particularly under environmental stress factors, such as high temperatures, which contribute to cells entering the VBNC state. The discussion reveals insights into the impact of stress factors on bacteria detection and the effectiveness of rqmicro.COUNT in such scenarios.
Benefits, Challenges, and Practical Insights with rqmicro.COUNT
An outstanding benefit provided by rqmicro.COUNT is the short time to results, giving customers and operators an almost immediate overview of the status of their cooling system. This quick insight is a key benefit as it makes it easier to keep an eye on the system. Those involved in treating water, such as those at innowac, have found the technology very helpful. It helps them to understand how dosing and water biology interact and makes their dosing strategies more precise.
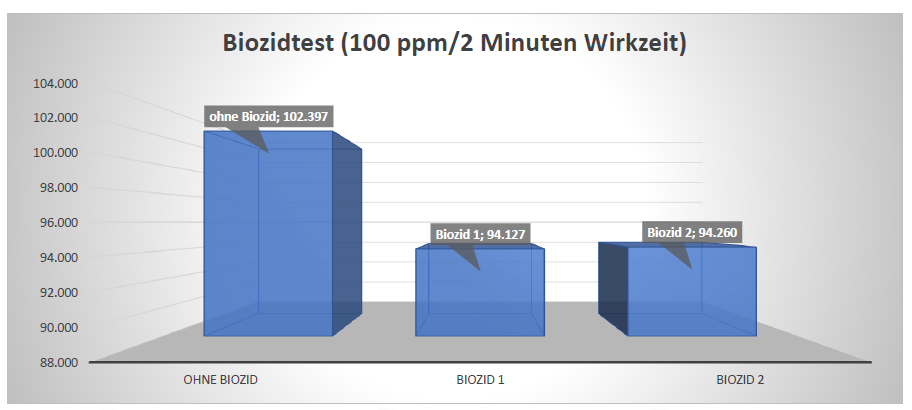
Picture 3: Biocide testing at innowac
Interpreting the results, sometimes with assessing flow cytometry charts (dot plots), and optimizing sample preparation to assure smooth analysis even in very complex water samples, took some time to getting used to. But with training and support from rqmicro team, innowac was up and running after a short time.
In the midst of these challenges, rqmicro.COUNT offers significant advantages. It is not just about numbers; it is about seeing the effect of treatments on bacteria. This visual representation makes the information easier and more practical, especially for those who cannot get into the details of Legionella and cooling water bacteria. Working with rqmicro.COUNT is not only about getting results quickly, but also about making complex data easy to understand so they can make better decisions about managing systems.
Looking Ahead: The Future with rqmicro.COUNT
As the presentation concludes, Philipp expresses satisfaction with rqmicro.COUNT and its positive impact on innowac's services. He emphasized that, with some guidance, anyone can manage the device, making it a valuable asset even for those without extensive laboratory experience.
Time savings, the ability to visualize results, and the device's reliability emerged as significant advantages. Challenges, such as interpreting results and working with flow cytometry charts, were navigated successfully, contributing to the overall success of the technology.
This journey has equipped innowac to offer enhanced possibilities to their customers and further explore the potential of this innovative technology.
To view the recorded version of the webinar, please click on the link below to request a recording.
